SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
Completion requirements
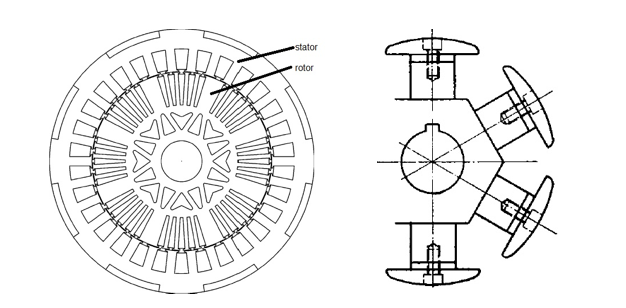
In synchronous motors, the circular frequency coincides with the circulating magnetic field. There are two types of synchronous motors based on the method of rotor excitation, ones with an excitation winding and ones excited by permanent magnets. In the first one, the rotor is equipped with a winding that is supplied with direct current. The rotor can be smooth or with salient poles.
This design’s advantage is that a wide range of constant maximum power is achieved due to the variation of direct current.
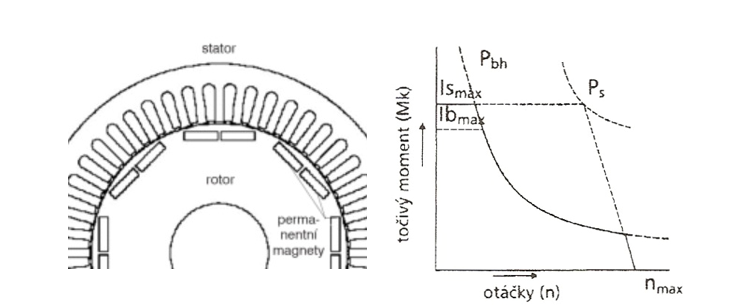
In permanently excited synchronous motors, the magnetic field in the rotor is excited by permanent magnets, which eliminates the need for additional electrical energy. The advantage of this design is its small size and high efficiency.