INTRODUCTION TO FUEL CELLS
There are different types of fuel cells that can be differenciated mainly by the electrolyte type and process temperature. The systems use different chemical reactions happening on electrodes and the efficacy of electrochemical conversion.
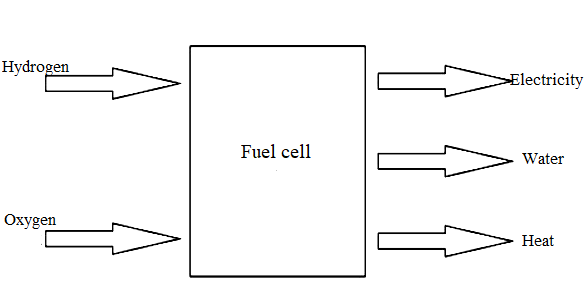
The principle of electricity production is based on chemical reactions between hydrogen and oxygen. This reaction produces energy and water. The energy comes in the form of an electric current. Function of all fuel cells is based on the identical principle Fig. 14. If we look back at the electrolysis hydrogen production, we will see that the fuel cell works similarly. In this case, the input substance is hydrogen, and the outcome is electric current. Hydrogen is pumped to the anode. The process splits hydrogen into anions and cations [12].
[12] 2H2 ⟶ 4𝐻+ + 4e−
The electrolyte allows the flow of protons but prevents the flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode. Electrons have to access the cathode through an external circuit. The flow of electrons via this circuit produces an electric current. Afterwards, the air is led to a cathode, where it is combined with hydrogen ions, and together they produce water and heat Fig. 13.
The overall reaction in a fuel cell is shown in Fig. 14.
[14] 2𝐻2+𝑂2 ⟶ 2𝐻2𝑂
The voltage in a fuel cell is very low, around 1 V. It has to be much higher to be used in practice. To achieve that serial connecting of multiple fuel cells is used.